Point of sale Definition:
A Point of Sale (POS) system includes software and hardware that helps businesses manage sales, inventory and customer transactions more efficiently.

What is POS?
A point of sale (POS) system describes a tool-combinational of hardware and software that businesses use to process payments and track transactions. A Point of sale system now functions digitally as a register that keeps track and manages orders management, processes payments, maintains inventory and analyzes sales trends.
POS solutions differ from traditional retail outlets to websites to smartphone apps. In addition to all these, they refer to web-based checkout systems.
What Does POS System Stand For?
POS stands for Point of Sale. It refers to the place or system where a purchase, actualized at the retail end of a selling process, is completed between a customer and a business. Simply put, it is the actual point at which money is exchanged for a service or a commodity in simple words; where payments are processed, a sale is recorded or a receipt is issued.
Key Takeaways of a POS System
- Point of sale in a business is a way to process payments and consummate the purchase in person or via the Internet.
- They usually generate receipts electronically or on paper.
- point-of-sale software keeps track of inventory management, pricing, and customer information for the marketing analysis side street.
What Does POS Mean?
The term POS, short for point of sale, refers to the place and system where a transaction is completed between a customer and a business. But today, when we talk about the POS meaning, we’re talking about much more than just a checkout counter. A modern POS system combines software and hardware to handle payments, track inventory, manage customer relationships, and provide valuable sales insights. Simply put, the POS system meaning has expanded; it’s now a central tool that helps businesses run more efficiently, make smarter decisions, and enhance the customer experience.
Key Components of a POS System
Hardware:
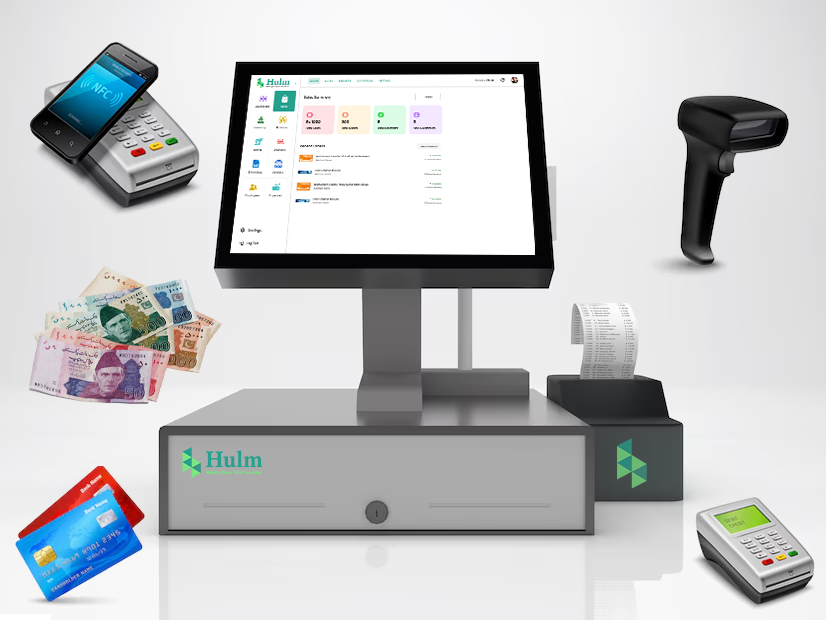

HulmSolutions POS Hardware
- Point-of-sale Terminal: The computer or device where the transactions are processed.
- Card Reader: For accepting credit and debit card payments.
- Barcode Scanner: Speeds up checkout by scanning product codes.
- Receipt Printer: Provides printed proof of purchase.
- Cash Drawer: Safely stores cash payments.
Software:
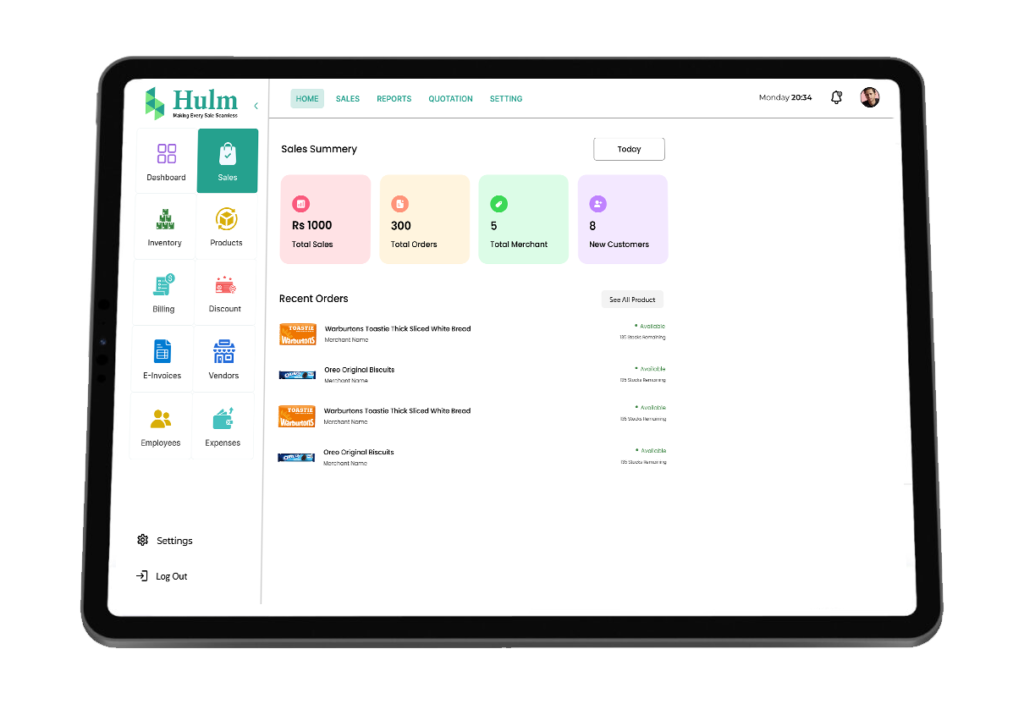
HulmSolutions Point of Sale (Dashboard)
- Handles payments, generates receipts and tracks sales data.
- Monitors stock levels in real time and automates restocking alerts.
- Generates sales reports and customer insights.
- Integrates with other business tools like accounting software.
- Accepts multiple payment methods, including cash, cards and digital wallets.
POS Market Growth & Future Trends
The global POS (Point-of-Sale) market is growing fast, expected to reach $110+ billion by 2032 (Fortune Business Insights). Businesses are choosing POS systems to speed up sales, manage inventory, and accept mobile or contactless payments, helping improve customer service. Studies show POS can boost sales by up to 46% in some industries (HotelTechReport). Top companies like Square and Lightspeed process billions in payments each year (Square, Lightspeed). Governments also support digital payments for better tax tracking (U.S. SBA, Commerce.gov). A modern POS isn’t just helpful—it’s now essential for business growth.
Why Is Point of Sale Important?
The point-of-sale system is the core of retail and service-based businesses, managing sales, inventory, customer data, and reporting. It is much more sophisticated than traditional cash registers, using modern technology to operate quickly and accurately, and interact nonstop with customers.
How Many Types of Point of Sale Software?
Not all point-of-sale systems are created equal. Depending on your business needs, you can choose from various Point of Sale software types, each offering unique features.
Traditional POS Systems
Traditional point-of-sale systems essentially describe the type of terminal where individual touchpoints are fixed in-store. These systems are reliable and secure but are not as flexible as modern solutions.
Cloud-Based POS Systems
Cloud based POS systems collect data online, and with an internet connection, you can access it from any of the device. They’re affordable yet scalable and put your best foot forward for multi-site business establishments.
Mobile POS (mPOS)
Portable Systems that run on a smartphone or tablet are ideal for small businesses, food trucks, or events. They allow transactions to be processed at the site.
Self-Service Kiosks
These kinds of systems enable customers to do the transaction themselves and generally are found in many fast-food and retail stores. Reducing wait times along the way enhances the overall level of customer experience.
Industry-Specific POS Systems
Some Point of Sale software is tailored for specific industries:
- Pos system for retail shop
- Pos systems for restaurants
- Pos system for hotels
- Pos systems for food trucks
- Pos systems for liquor stores
- Pos system for cafes
- Pos system for schools
- Pos system for pharmacy and medical store
- Pos system for salon
- Pos system for hospital
- Pos systems for supermarkets
- Pos systems for bars
How Does Point of Sale Work
A POS works by processing customer payments, recording sales transactions, managing inventory, and generating real-time reports for seamless business operations.
Set Up the POS Hardware
- Make point-of-sale terminal connections with the accompanying hardware, such as barcode scanners, card readers, and printers.
- Also, try to provide a reliable internet connection for the web-based systems.
Configure the POS Software
- Load up the product catalog with all compulsory descriptions, prices, and stock levels.
- Set up tax rules and the modes of payment, such as cash, cards, and mobile wallets.
- Create the profiles of employees and assign them access permissions.
Process Transactions
- Scan products or select services from the terminal.
- Apply for discounts or promotions if applicable.
- Accept payments through cash, card or digital wallets and issue receipts.
Use Analytics to Enhance Efficiency Operations
Most modern point-of-sale systems supply real-time statistics about selling trends, stock levels, and customer preferences. Therefore, they can be used for business decision-making.
Train Your Team
Do not forget to train the staff on how to operate the POS system efficiently. Most of them offer various training resources and customer support as needed.
How to use POS System
A modern POS (Point of Sale) system is designed to make day-to-day operations faster, easier, and more accurate. Whether you’re ringing up sales or managing inventory, the process is straightforward once you’re familiar with the flow. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how to use a POS system effectively:
1. Log In and Set Up Your Shift
Have a login on the POS terminal under the assigned credentials of the individual. Depending on your system, you may need to open a cash drawer or start a shift to correctly track sales and transactions.
2. Add Items or Select Items to be Sold
Scan a barcode, search for an item by name, or simply tap the product on your POS. It should allow the quick building of the customer’s order. For services, select the appropriate options, time slots, or engaged staff.
3. Apply Discounts or Promotions
Before completing the sale, apply all current promotions, coupon codes, or custom discounts. Most POS systems allow you to do this with one click in order to maintain speed and consistency.
4. Select the Payment Method
The moment the order is ready, the POS shall provide all acceptable means of payment, such as cash, credit or debit cards, mobile wallets, or gift cards. A modern POS is even able to accept split payments via contactless solutions, affording customers further ease.
5. Issue Receipt
Print and hand over the receipt after the transaction, or offer to email or SMS the receipt to the customer for their convenience. Encouraging digital receipts can go a far way in reducing paper usage, while also helping build a customer database for marketing opportunities.
6. Update Inventory Real-Time
Upon successful completion of sales, your inventory is automatically updated. Real-time syncing helps prevent over-selling, track stock movement, and timely planning of reorders without manual counting.
7. Capture Customer Information
Quite a few systems let you quickly create or update customer profiles at checkout, whereby you can log in names, emails, purchases, and preferences. This information may come in handy for loyalty programs, follow-ups, and targeted marketing.
8. Access Reports and Analytics
You can instantly view detailed summaries of sales, employee performance, top-product trends, and customer insights from the dashboard whenever you want. These reports become imperative to sustain decision-making, thereby growing the business.
Benefits of a Point of Sale System
- Better Transaction Accuracy: Decrease human error, thus ensuring price and payment correctness.
- Real-Time Inventory: It enables automatic monitoring of inventory levels to prevent stockouts and overstocking.
- Quicker Checkouts: It hastens checkout, which minimizes the hours customers have to spend in queues and, as a result, increases their satisfaction.
- In-depth Reporting and Analysis: Comprehensive reports are generated concerning sales, customers, and performance for informed decisions.
- Better Customer Experience: It leads to personalized services, loyalty programs and faster transactions.
- Multi-Payment Mode: It accepts payment in a variety of means, including credit/debit cards, mobile wallets, or contactless payments.
- Seamless Access to Other Domains of Business Tools: This makes integration with the accounting, e-commerce applications and also CRM systems.
- Employee Management: Improved accountability with an integrated tracking of employee sales, attendance and access rights.
- Security and Data Protection: Secure and encrypted access protocols ensure the protection of customer and transaction data.
- Flexibility: It adapts easily to the growth of a business and can hence be used at many locations with newer integrations.
Point of Sale Features
- Inventory Management
- Purchase Orders
- Payment Processing
- Employee Management
- CRM
- Sales Tracking & Reporting
- Vendors Management
- Billing Management
Future Trends in POS Technology
Continuous evolution in technology keeps on making POS systems more intelligent and versatile. The future of POS, what do you expect?
- AI Insights: Deeper analytics and predictive modeling of customer behavior, inventory optimization.
- Contactless Payments: Proliferate digital wallets and QR code payments.
- IoT integration: Smart shelves and RFID tags for automatically updating inventories.
- Increasing mobile solutions: More micro businesses are adopting mPOS systems.
Conclusion
POS systems are more than just payment processing; they are systems of business change that may benefit businesses of all sizes. A good POS system may help retail stores, restaurants, and service providers optimize operations, improve customer happiness, and drive growth.
To select the best one for your business, you must be comfortable with the systems and their capabilities. It is as important for owners of small businesses to participate as it is for the management of big businesses to invest in a robust POS system to achieve performance and profitability.
To learn more about Point of Sale click here!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What Payment Methods Do POS Systems Support?
Ans. Point of Sale systems support cash, credit/debit cards, mobile payments, and contactless payment methods.
Q2. What Types of Businesses Use point-of-sale systems?
Ans. POS systems are used by retail stores, restaurants, hotels, salons, and other businesses that handle transactions.
Q3. How Can Consumers Report Point of Sale Fraud?
Ans. Consumers can report point-of-sale fraud to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) via its Consumer Sentinel Network.
Q4. What Are the Key Features of a Modern point-of-sale system?
Ans. Modern POS systems include payment processing, inventory tracking, sales reporting, and customer data management.
Q5. Why Are Point of Sale Systems Important for Businesses?
Ans. POS systems streamline operations, reduce errors, track sales, and improve customer service.
Q6. How Do Retailers Prevent POS Fraud?
Ans. Retailers use PIN verification for debit cards, CVV codes for online payments, and secure payment technologies to prevent fraud.
Q7. How Secure Are POS Transactions?
Ans. Point of Sale transactions are secured through encryption, tokenization, EMV chip technology, and regular software updates.
Q8. What Is a Cloud-Based POS System?
Ans. A cloud-based Point of Sale system stores data online, allowing businesses to access it from any device with internet connectivity.
Q9. How Does Point of Sale Systems Improve Inventory?
Ans. Point of Sale systems track real-time inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and help businesses plan restocking efficiently.
Q10. What Was the First Point of Sale System?
Ans. The first Point of Sale system was the cash register, invented in 1879 by James Ritty. It was later sold to National Cash Register (NCR), which popularized its use.
For More Information About Point of Sale Click Here!